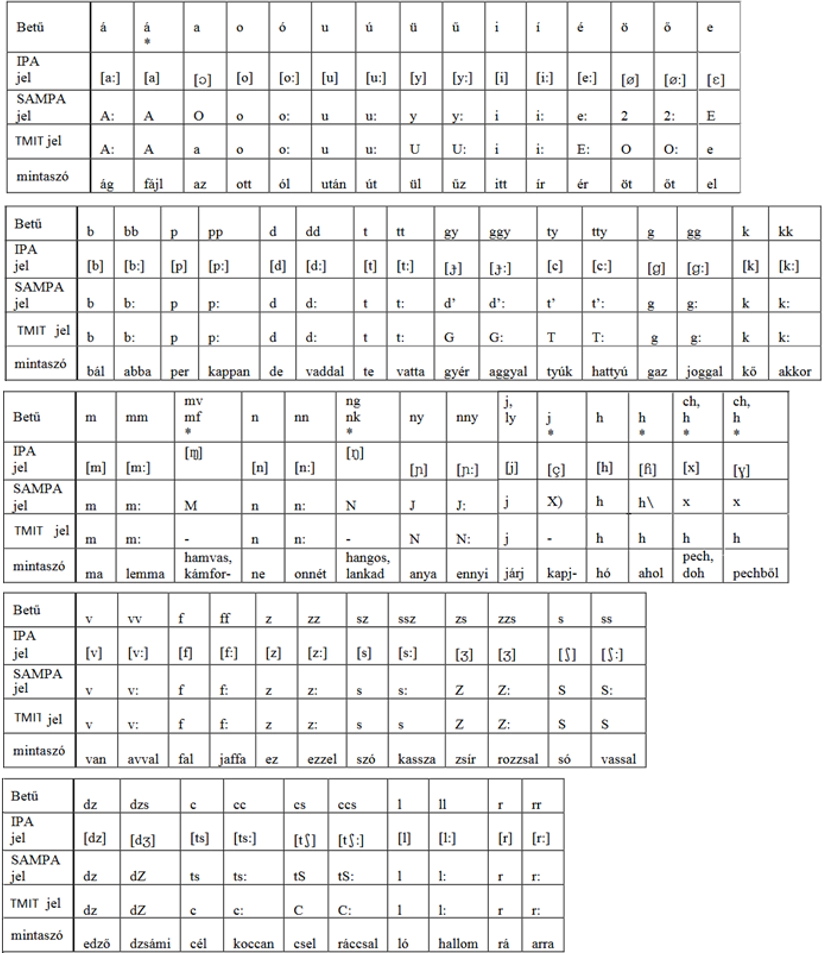
Hungarian speech sound symbols
Sound symbols were invented to clearly mark speech sounds in textual materials. The sound symbols represent the sounding versions of phonemes and phoneme variants. With this sound marking, we can specify the pronounced sound, regardless of which letter (combination) corresponds to it in writing. The speech sound symbols thus also express the pronounced speech sound internationally. The first phonetic system was created in 1889 by the International Phonetic Association. This is the IPA symbol set. Later, the sound symbols expressed by characters, which can also be used on computers, were developed. This is the SAMPA symbol system. The BME TMIT hungarian speech sound symbols were developed for specific Hungarian research, mainly computer research for speech synthesis. The phoneme variants are marked with an asterisk under the letter. For example, the short version of the Hungarian á sound is also marked with an asterisk. The short á is not marked with a letter in Hungarian texts (e.g. bájt/byte, fájl/file), but it is pronounced.