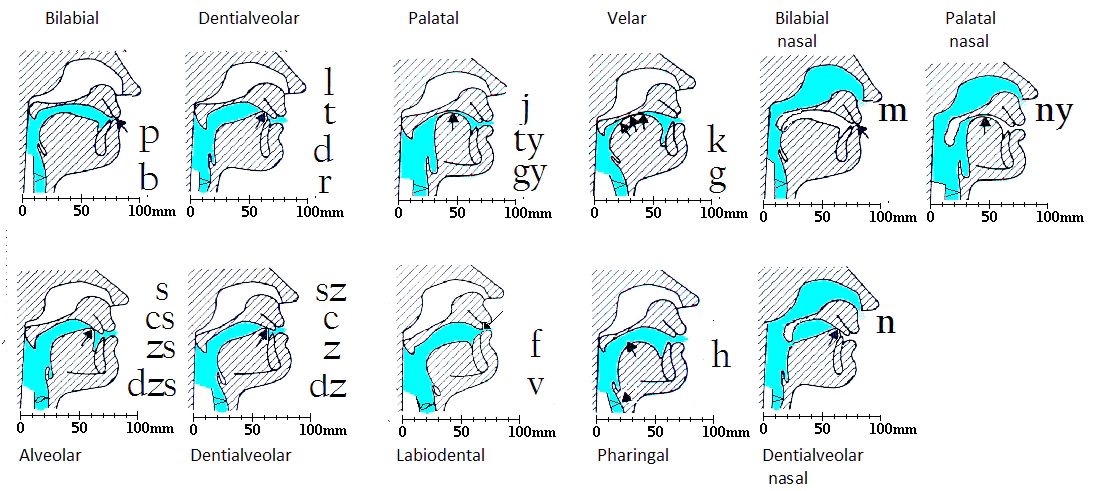
Articulatory organs
Speech is formed by continuous articulatory movements from the voice produced by vocal cords in the larynx. The articulation channel extends from the larynx to the lips, with an average length of 14 cm for women and 17 cm for men. Articulation movements are fast. The articulation speed of Hungarian speech is on average 13 speech sounds per second. The following articulatory organs are involved in the formation of different speech sounds: larynx, soft palate, uvula, tongue, hard palate, tooth bed, teeth, lips and jaw.
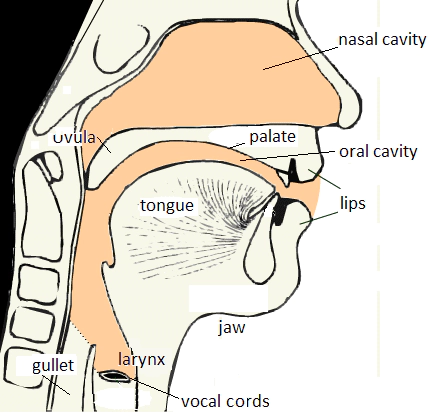
The articulatory organs, used during the articulation of Hungarian vowels are:
- Jaw (open, half-open, half-closed, closed positions)
- Lips (unrounded or rounded forms)
- Tongue (vertical and horizontal positions)
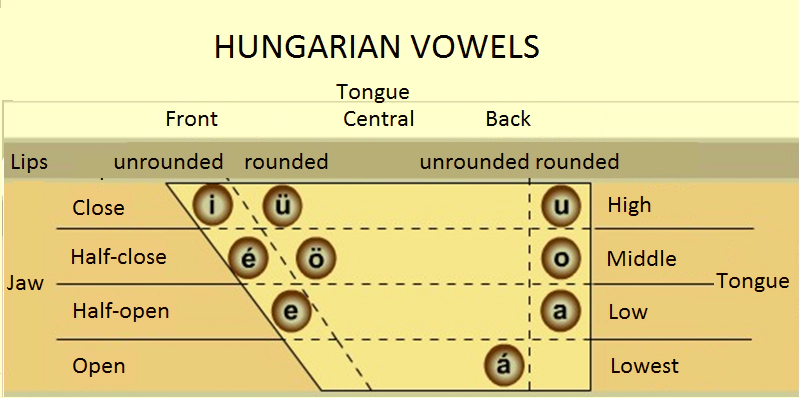
Articulation positions of Hungarian speech sounds
In the case of voiced speech sounds, the vibration, produced in the larynx (fundamental voice) is very similar independently of the pronounced voiced speech sound (by the same person). The radiated speech sound will be formed from the fundamental voice sygnal by the articulation.
The articulation of the Hungarian vowels.
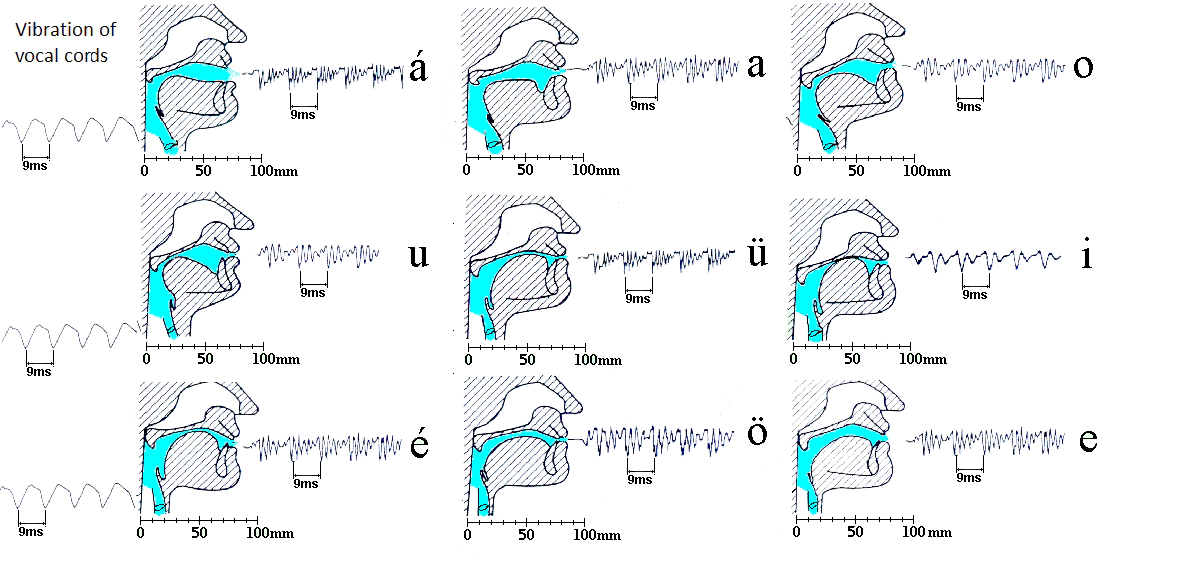
The articulation of the Hungarian consonants.