Excitation forms
One of the basic factors in the creation of speech sounds is the excitation, i.e. the sound source from which the actual speech sound is formed as a result of articulation. There are basically three types of the excitation: viced, noisy, and mixed. Vocal excitation is a regularly repeating sound period. This signal is created in the larynx as a result of the operation of the vocal cords. The place of excitation of this fundamental voiced sound is constant.
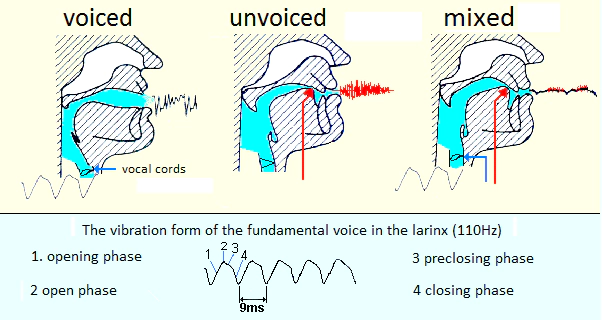
Purely noisy excitation is an aperiodic vibration that can occur at different points in the articulation channel (larynx or oral cavity). A so-called mixed excitation occurs when a mixture of the former two forms are present at the same time.
The energy for the excitation sound is provided by the air flow expelled from the lungs.
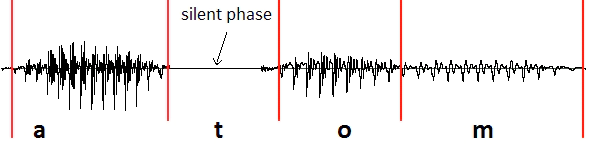
A special type of excitation is the so-called silent phase (no audible excitation signal is present inside the speech sound). The silent phase is an important component of certain speech sounds (p, t, k etc). In the silent phase, the oral cavity is closed and the vocal cords are open.